On March 3, the General Office of the Communist Party of China Central Committee (hereinafter referred to as the CPC Central Committee Office) and the General Office of the State Council (hereinafter referred to as the State Council Office) jointly issued the Guidelines on Building a Modern Environmental Governance System (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines), requiring all regions and departments to implement the guidelines in accordance with local conditions.
The Guidelines emphasize a government-led, enterprise-driven, and socially participatory environmental governance framework, clarifying the responsibilities of governments, enterprises, and the public. For enterprises, the document specifies requirements such as implementing pollutant discharge permit systems, advancing green production practices, enhancing pollution control capabilities, and disclosing environmental governance information. These provisions not only set baseline standards for pollution management and transparency but also establish benchmarks for enterprises to provide resource-efficient and eco-friendly products/services and adopt sustainable production methods.
To strengthen the environmental governance market system, the Guidelines propose bolstering the environmental protection industry by:
l Accelerating independent innovation in key environmental technologies.
l Promoting the demonstration and application of first-of-its-kind (FOAK) environmental equipment.
l Supporting industry leaders, specialized mid-sized firms, and niche SMEs.
l Encouraging enterprises to participate in the Green Belt and Road Initiative to export advanced environmental technologies and equipment.
As the cornerstone technology for clean and efficient coal utilization, coal gasification plays a pivotal role in the coal chemical industry chain. Among these technologies, Circulating Fluidized Bed Coal Gasification (CGAS) has gained significant market traction due to its broad coal adaptability, high heat transfer efficiency, and scalability. As the industrialization platform for the Hongguang Initiative project "Industrialization of Circulating Fluidized Bed Coal Gasification Technology", ZHGAS has successfully applied CGAS in coal-to-synthesis gas and coal-to-clean gas production, aiming to deliver high-quality demonstration projects with economic, social, and environmental benefits.
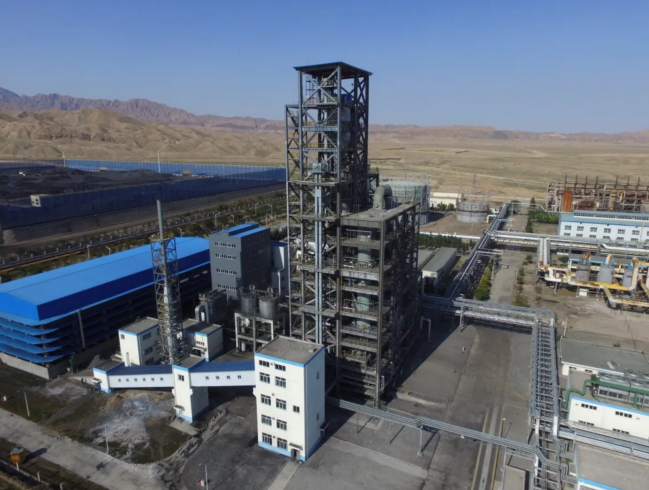
In December 2019, ZHGAS commissioned its first CGAS demonstration project—the Lanshi Jinhua 1,000-ton Circulating Fluidized Bed Pressurized Gasification Plant—marking China’s inaugural application of clean circulating bed gasification technology in the synthetic ammonia industry. This also marks China’s inaugural demonstration project for low-rank pulverized coal pressurized gasification using circulating fluidized bed (CFB) technology. This project converts local low-rank coal in Jinchang into clean syngas, reducing gas production costs by 30–50%, eliminating wastewater and exhaust pollution from traditional gasifiers, and saving the enterprise nearly 50 million annually. CGAS offers a breakthrough solution for the synthetic ammonia sector’s environmental challenges.

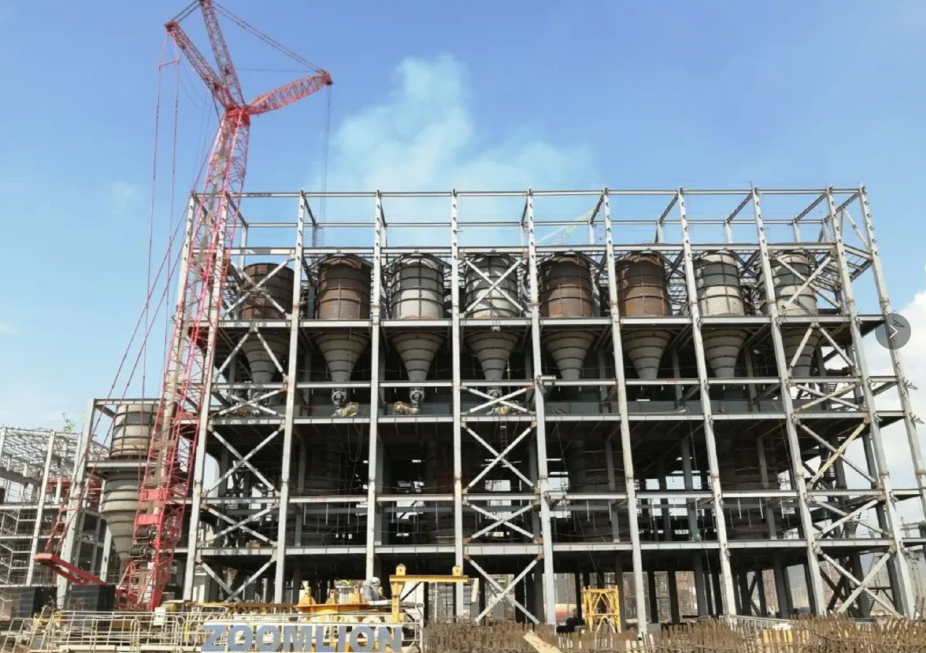
CGAS technology has also expanded internationally under the Belt and Road Initiative. For example, the Xiamen Xiangsheng Circulating Fluidized Bed Oxygen-Rich Gasification Project in Kendari City, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia, will supply fuel for a 2.5-million-ton stainless steel plant. Upon completion, this plant will supply fuel to thirty-two nickel-iron production line rotary kilns across four workshops at the smelter. Once operational, this gasification plant is set to become the world's largest circulating fluidized bed gasifier system in the steel industry, with its gasification efficiency projected to exceed 75% and overall thermal efficiency also surpassing 84%.

In recent years, China has introduced a series of intensive environmental protection policies, continuously intensified enforcement efforts. Meanwhile, policy measures have evolved from administrative approaches to legal and economic instruments, making third-party pollution governance an irreversible trend.
Recent policies related to the environmental protection industry in China
Release Time | Issuing Authority | Laws And Regulations | Main Content |
2016 | Ministry of Environmental Protection | Guidance on Leveraging Environmental Protection to Facilitate Supply-Side Structural Reform | To strengthen environmental hard constraints and facilitate the elimination of backward and excess production capacity; strictly enforce environmental access requirement to enhance the quality of new production capacity; implement environmental governance tasks to drive the growth of the environmental protection industry; and advance innovation-driven development while refining supporting policies. |
2017 | Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development | Notice on Accelerating Municipal Solid Waste Sorting in Key Cities | By the end of March 2018, all 46 key cities were required to formulate Implementation Plans for Domestic Waste Sorting Management or action plans, specifying annual work targets, detailing work contents, and quantifying work tasks. |
2017 | Central Military Commission of the CPC | Directives on Implementing Waste Sorting Systems in Military Units | By the end of 2020, military units were required to fully implement domestic waste sorting systems, with the overall recycling rate of household waste reaching over 35%. |
2018 | Ministry of Ecology and Environment | Draft Amendment to China's Solid Waste Pollution Prevention and Control Law (Call for Comments) | The state implements a domestic waste sorting system. Local governments at all levels shall establish classified disposal systems covering sorting-at-source, segregated collection, specialized transportation, and categorized treatment. They must adopt methods tailored to local conditions, deploy corresponding facilities and equipment, promote full utilization of recyclables, and achieve reduction, recycling, and harmless treatment of domestic waste. |
2019 | Seven departments including the Ministry of Science and Technology, People's Bank of China, National Financial Regulatory Administration... | Catalog of Green Industries (2019 Edition) | The Directory encompasses six major categories: energy conservation and environmental protection, clean production, clean energy, ecological environment, green upgrading of infrastructure, and green services. It further delineates 30 secondary classifications and 211 tertiary classifications, with each tertiary category accompanied by detailed explanatory notes and defining criteria. This represents the most comprehensive and detailed guidance currently available in China for defining green industries and projects. |
ZHGAS has consistently adhered to a “customer-first” philosophy, proactively aligning with industry trends and policy shifts. By integrating R&D with industrial demands and addressing practical production challenges, ZHGAS applies CGAS technology across sectors through technology integration, system optimization, engineering development, and market-oriented promotion, driving the commercialization of R&D achievements.
To date, ZHGAS has successfully implemented fixed-bed gasification system upgrades for coal-to-synthesis gas and coal-to-clean gas production. Concurrently, it has initiated CGAS deployment in coking, alumina, and lime industries. Moving forward, ZHGAS will expand its market presence and accelerate CGAS applications in:
Integrated three-waste treatment (waste gas, water, residues),
Harmless treatment and resource utilization of multi-category hazardous waste,
Low-energy, low-cost sludge harmless disposal.
These efforts will deepen technology commercialization, deliver clean energy solutions to industries, and foster diversified, sustainable growth in environmental protection and coal chemical sectors.